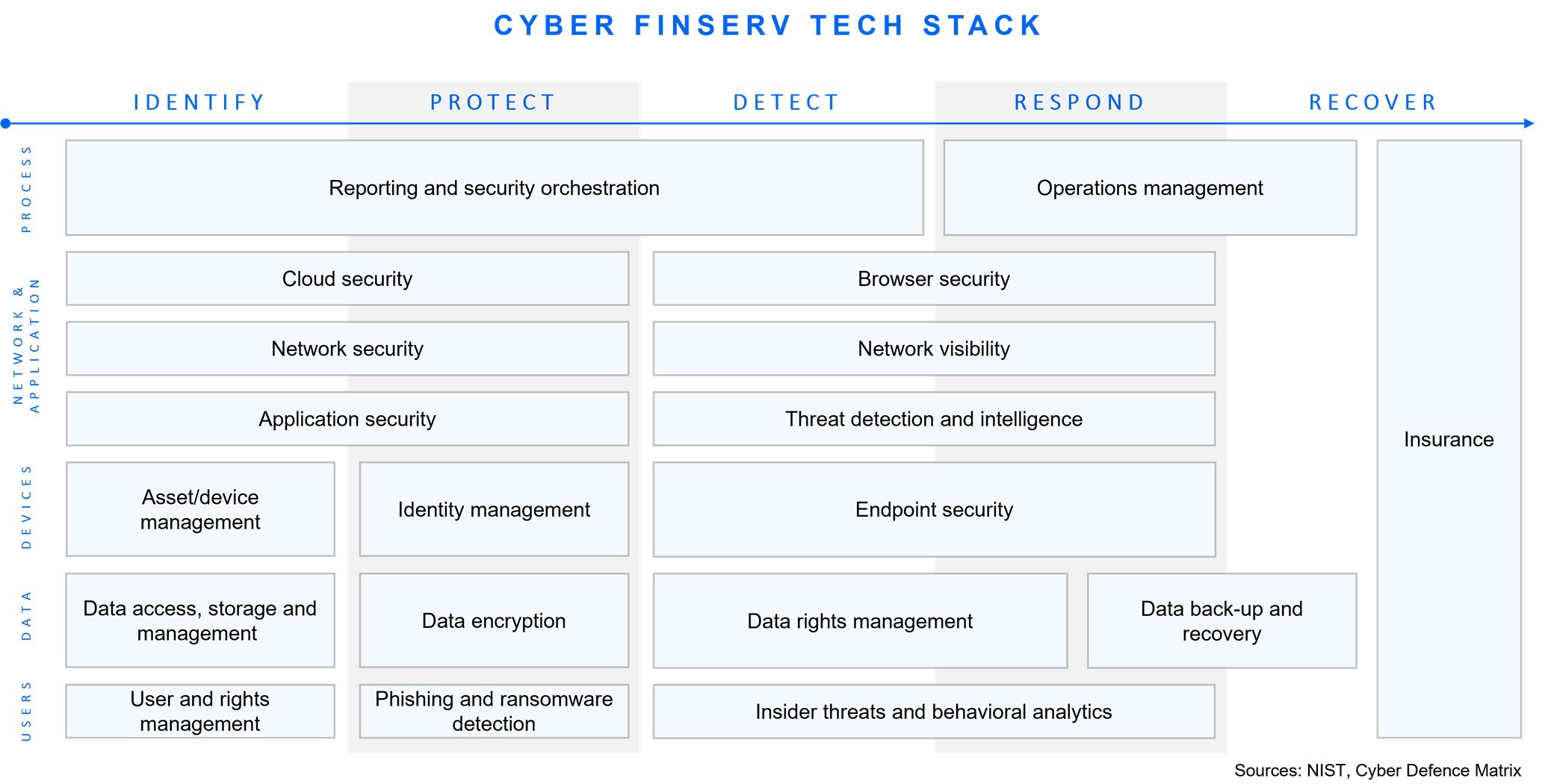
The safe and secure operation of Financial Services (FinServ) markets and infrastructure is essential for maintaining financial stability and fostering economic growth.
With a per-company cybercrime cost that is 40% higher than average compared to non-financial sectors, cyberthreats within FinServ are axiomatic in nature: not a question of if, but when.
The rise of cloud computing, SaaS and API-driven tech stacks have exacerbated the interdependencies between FinServ and FinTech, and their respective customer bases. Each wave of FinTech innovation also unlocks opportunities for new cyber innovations and cyber FinTech market growth.

As such, the cyber FinServ tech stack will continuously evolve. Cyber risks in FinServ and FinTech are ever-present and evolutionary in nature, resulting in a continuously shifting threat landscape that requires agile solutions and a layered tech stack to effectively manage emerging risks posed by new assets, new technologies and new actors.
At MiddleGame Ventures, we believe the themes (and incorporated technologies) highlighted below will play a pivotal role in the evolution of cyber solutions for FinServ and FinTech, including: